Authors: John Campbell, Priti Upadhyay, and Jonny McElhinney
Digital twins technology, powered by advanced simulation platforms such as the Unreal Engine, is revolutionizing the creation and management of training data for deep learning models. Traditional data collection and manual labeling for Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) detection are often time-consuming, costly, and prone to human error. Moreover, capturing diverse real-world conditions, such as varying lighting conditions, worker movements, and different types of PPE, can be challenging and sometimes hazardous.
To overcome these challenges, our digital twin approach enables the generation of synthetic, accurately labeled datasets. We perform this in a fully controlled virtual environment. The platform allows extensive customization. This includes adjustable lighting conditions, diverse avatar animations, flexible PPE configurations, and dynamic camera placements to simulate multiple real-world perspectives. In this post, we cover the following:
- Discuss the advantages of using synthetic data for training and validation
- Outline the architecture of our digital twin simulation platform
- Describe the demo environment used for validating model performance
- Highlight how this approach accelerates model development while improving safety and scalability
Background
In industrial environments, safety is the foundation of smooth and efficient operations. The safety of workers is directly linked to the overall safety and productivity of the industry itself. When workers are protected, processes run without disruption, equipment is used responsibly, and costly accidents are avoided. Among the many factors that contribute to industrial safety, the correct use of PPE stands out as one of the most critical.
However, maintaining consistent PPE compliance across large industrial sites can be challenging. Human error or time pressure can result in workers failing to wear essential protective gear. This includes items such as hard hats, gloves, safety glasses, or vests. These lapses not only endanger individuals but can also lead to serious incidents, production downtime, and regulatory penalties that affect the entire operation.
To address this challenge, industries are increasingly adopting PPE detection technology. Using artificial intelligence (AI) and computer vision, these systems automatically detect whether workers are wearing the required PPE in real time. They can alert supervisors, log compliance data, and help companies maintain a culture of safety and accountability.
Real-world data challenges
Collecting real-world data from industrial sites for training PPE detection models presents several challenges. Capturing images and videos of workers wearing PPE in different scenarios can be time-consuming, expensive, and potentially hazardous. There are also privacy concerns, as recording employees raises ethical and legal issues. Furthermore, real data often suffers from imbalances and biases. Certain types of PPE, worker demographics, or lighting conditions may be underrepresented, leading to models that perform poorly in these scenarios.
Another significant issue is human labeling inconsistency, where manual annotation of PPE in images can be error-prone and subjective. This results in mislabeled or inconsistently labeled data that negatively impacts model accuracy. Enter the game-changer: Digital twin technology unlocks unparalleled problem-solving power. By creating highly realistic virtual replicas of industrial environments, digital twins enable the generation of large volumes of diverse, labeled, and unbiased data safely and efficiently. Synthetic data from digital twins ensures balanced representation across PPE types, worker appearances, and environmental conditions. Thus, overcoming the limitations of real-world data while reducing risks, costs, and compliance challenges.
By integrating PPE detection into safety management systems, industries can move from reactive responses to proactive prevention. It ensures that worker protection becomes a continuous, automated process, reinforcing the idea that the safety of every worker is essential to the safety and success of the entire industry.
Synthetic data generation
A digital twin of a real-world industrial environment enables organizations to simulate numerous workplace scenarios safely and efficiently. Using advanced 3D modeling, physics engines, and visual rendering from gaming technology, synthetic data can be generated to represent workers wearing different types of PPE in various conditions, lighting, and poses. This synthetic data becomes a valuable training resource for deep learning (DL) models. It enables them to recognize PPE more accurately and reliably. By leveraging digital twins, industries can create realistic, labeled datasets at scale. Thus, accelerating the development of robust PPE detection algorithms without disrupting actual operations or exposing workers to risk.
At SAS, we have developed a digital twin platform utilizing the advanced capabilities of Unreal Engine. It was specifically designed to support the creation and training of PPE detection models for industrial safety applications. This digital twin serves as a highly realistic virtual environment that mirrors real-world industrial settings, including factories, construction sites, and warehouses. This platform enables the simulation of diverse workplace conditions. This would include things such as dynamic lighting, realistic worker movements, and complex environmental factors that are difficult or hazardous to capture in real-world settings, as shown in Figure 1 below.

Our digital twin features customizable worker avatars. They can represent individuals of diverse body types, skin tones, ages, and genders, helping to eliminate demographic bias in data generation. Each avatar can be configured to wear or omit specific PPE items such as hard hats, gloves, safety glasses, and safety vests. As shown in Figure 2 below, this allows us to simulate countless combinations for accurate model training. The system also incorporates environmental dynamics, including lighting changes, camera perspectives, and background variations, ensuring that the synthetic data closely mimics real-world variability.

A key advantage of this approach lies in automated and consistent label generation. See Figure 3 below. The system takes a JSON input containing customized parameters for avatars and their PPE configurations, such as hard hats, vests, gloves, and safety glasses. With this flexible setup, users can easily create diverse and realistic scenarios using a random scenario generator. This approach enables efficient dataset balancing, allowing targeted data generation for underrepresented PPE classes or specific conditions where the detection model underperforms. Every synthetic image produced within the digital twin is automatically annotated with precise metadata. This includes the type, location, and state of PPE. Bounding boxes are generated solely for the visible portions of the objects within the rendered scene, with occluded regions excluded from annotation.
This level of labeling accuracy and consistency is extremely difficult to achieve with manual annotation of real-world data, which is often prone to human error and subjective interpretation. By generating perfectly aligned and error-free labels, we ensure that our deep learning models are trained on reliable, standardized data. This significantly improves detection accuracy, reduces training time, and enhances the model's overall robustness.
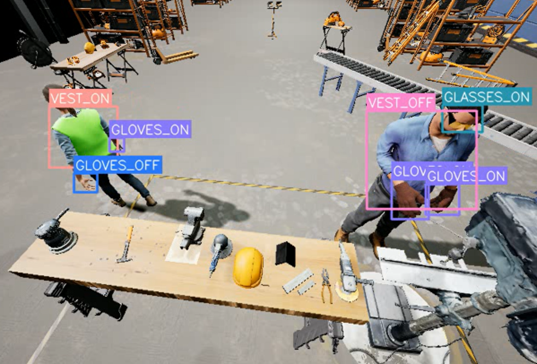
With these features, our digital twin not only accelerates data generation but also ensures fairness, consistency, and precision. Creating a solid foundation for developing advanced, bias-free, and dependable PPE detection systems strengthens industrial safety.
PPE detection model
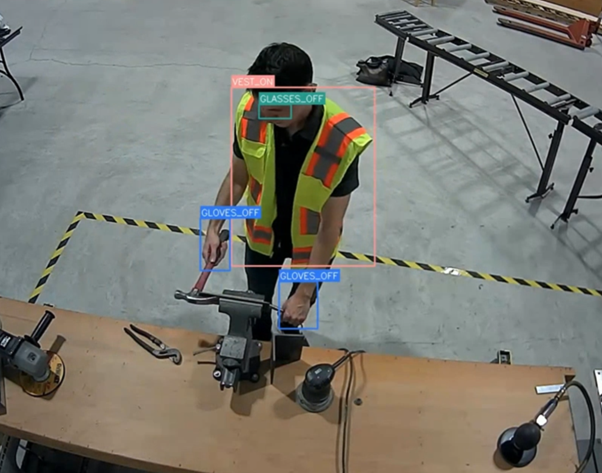
To validate and fine-tune our PPE detection solution, we have created a demo physical environment at SAS. This space closely mimics a real industrial workspace. See Figure 4 below. This controlled setup features actual machinery, workstations, and safety zones. It also includes strategically positioned cameras that capture worker movements and PPE usage from multiple angles. By deploying our AI models and digital twin–generated scenarios in this environment, we can achieve several objectives. These would include observing system performance in real-world conditions, identifying potential blind spots, and optimizing detection accuracy. The demo environment also allows us to test alerts, workflows, and integration with SAS Event Stream Processing, ensuring that the solution functions seamlessly before scaling it to full industrial sites. This hands-on approach provides critical insights, bridging the gap between simulated training data and actual operational deployment.

Using the data generated from our digital twin and validated through the demo physical environment, we trained a deep learning DETR (DEtection TRansformer) based object detection model to accurately identify PPE compliance in industrial settings. DETR’s transformer architecture enables the model to directly predict object bounding boxes and classes without requiring complex post-processing. This makes it highly effective for detecting multiple PPE items in cluttered or dynamic environments. By training solely on synthetic data that includes diverse worker poses, lighting conditions, PPE types, and demographics, the model learned to generalize well across different scenarios, as shown in Figure 5 below. The trained DETR model demonstrated high accuracy in detecting PPE, accurately identifying compliance or violations in real-time. These results confirm that synthetic data from digital twins can effectively train advanced AI models for reliable, bias-free PPE detection in industrial settings.
SAS ESP for deployment
To bring our PPE detection solution from development to real-world deployment, we are leveraging SAS Event Stream Processing (ESP). SAS ESP enables real-time ingestion, processing, and analysis of high-volume data streams from industrial sites. An example would be video feeds from cameras monitoring worker activity. By integrating our deep learning models with SAS ESP, we can instantly detect PPE compliance. Alerts are generated the moment a violation occurs. This streaming analytics approach enables the quick identification and resolution of safety incidents. Thus, it enhances both worker protection and operational efficiency. By combining advanced AI with SAS ESP, we are deploying a robust, real-time PPE detection system that turns data into actionable insights for safer industrial operations.
Summary
Ensuring industrial safety requires more than just providing protective equipment. It also depends on actively monitoring compliance and fostering a culture of accountability. PPE detection systems enhance industrial safety by ensuring that workers wear the necessary protective gear in real-time. This reduces accidents and operational disruptions. Digital twins and gaming technologies play a crucial role in generating large, diverse, and unbiased datasets for training machine learning models, thereby ensuring fair representation across various demographics, including skin tones, ages, genders, and others. The automated and consistent labeling provided by digital twins further strengthens model accuracy and reliability.
Finally, leveraging SAS Event Stream Processing (ESP) enables real-time deployment of these AI models on industrial sites. In other words, they instantly detect PPE compliance and generate alerts to prevent hazards. Together, these technologies create a comprehensive, proactive approach to industrial safety, protecting workers, enhancing compliance, and improving overall operational efficiency. Interested in learning more? Read more about the SAS Industrial Safety PPE model.
